Communication Process, Network Media & Protocols
Communication Process, Network Media & Protocols
Introduction
What is Communication
The communication process involves a series of steps or actions aimed at achieving successful transmission of information. It consists of various components such as the sender, the message, the encoding of the message, the receiver, and the decoding of the message.
Within the communication process, there are various channels of communication to take into account. These channels pertain to the means by which a message is transmitted. They encompass voice, audio, video, written email, fax, and even body language. The primary aim of the communication process is to deliver information to an individual or party and ensure comprehension. To accomplish this, the sender must judiciously choose the most appropriate medium for successful communication.
Communication Process
Component of communication
1. The fundamental elements of the communication process include:
Context -
Sender / Encoder -
Message -
Medium -
Recipient / Decoder -
Feedback -
Transmission Media
The transmission medium refers to a conduit through which information can be transmitted from a sender to a receiver. Positioned beneath the physical layer, the transmission media are regulated by the physical layer. They are commonly referred to as communication channels.
Transmission media are of two types −
Guided Transmission Medium
Unguided Transmission Medium
 |
| Types of Transmission media |
Guided Media
Guided Media denotes a form of communication medium that employs conducting material to facilitate the transmission of data or signals. This category encompasses various types of cables and wires, each possessing its own set of characteristics, including transmission speed and susceptibility to noise. Guided media is also commonly known as wired media, as it relies on the utilization of wires to convey data between different locations.
Types of Guided Media
Twisted Pair
Coaxial Cable
Optical Fiber
Twisted Pair Cable
Twisted pair cables, one of the earliest guided transmission media and also It is a very cheapest medium of communication, they are composed of two insulated copper wires twisted together and aligned in parallel. Body cover of cable is very thin, Each copper wire has a diameter of approximately 1mm, with one wire designated for data transmission and the other for grounding referencing purposes. This cable doesn’t provide security as the signals collapsed. This cable is used in local telephone lines.
Reason for Twisting
Noise, interference, and crosstalk are common challenges in all transmissions. When wires are twisted, some noise signals align with data signals, while others move in the opposite direction. This causes external waves to cancel each other out due to the varying twists. The receiver then calculates the voltage difference between the two wires to retrieve the data. This method leads to a significantly enhanced immunity against noise.
Applications of Twisted-Pair Cables
In telephone lines
In DSL lines
In LANs
Types of Twisted–Pair Cables
There are two types of twisted pair cables −
Unshielded Twisted Pair ( UTP ): These components usually consist of wires and insulators.
Shielded Twisted Pair ( STP ): The insulated wires are surrounded by a braided wired mesh for added protection.
 |
| Twisted-Pair-wire |
Coaxial cable
The diagram below provides a visual representation of the structure of a standard cable. The central conductor enables the flow of electrical signals. Coaxial cable is commonly employed by cable operators, telephone companies, and internet providers across the globe to transmit data, video, and voice communications to their customers. Additionally, it has been widely utilized within residential environments.
 |
| Coaxial-cable-Structure |
Optical Fiber
 |
| Optical-fiber-Structure |
Advantages of Optical Fiber.
higher bandwidth.
Less signal attenuation
Noise Resistance:
Disadvantages of Optical Fiber.
Cost. Fiber-optic
cable is expensive..
Unguided Media
In contrast to conventional systems that depend on physical conductors or metal, this technology utilizes the air as a medium to transport electromagnetic signals. Referred to as wireless media, it eliminates the requirement for any type of cable connection.
Radio Waves
 |
| Radio-waves-Transmission |
A radiating antenna is utilized in radio transmission to convert a time-varying electric current into an electromagnetic wave or field. This wave or field can freely propagate through a non-conducting medium, such as air or space. In the context of a broadcast radio channel, an omnidirectional antenna emits a transmitted signal that covers a wide service area.
Within a point-to-point radio channel, a directional transmitting antenna is employed to concentrate the wave into a narrow beam, which is targeted towards a single receiver site. Subsequently, the transmitted electromagnetic wave is received by a remote receiving antenna and transformed into an electric current.
Microwaves Transmission
Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic radiation that have wavelengths spanning from one millimeter to one meter, and frequencies falling between 300 MHz (megahertz) and 300 GHz (gigahertz). They are a component of the wider electromagnetic spectrum and find widespread use in a variety of applications.
Features of Microwaves
Microwaves propagate in straight lines, therefore, it is crucial for the transmitter and receiver stations to be precisely aligned with each other. Line-of-sight propagation is essential for the towers hosting the stations to ensure that communication is not obstructed by the curvature of the earth or any other obstacles.
One prominent application of microwaves is in microwave ovens, which use microwave radiation to heat food quickly and efficiently. These ovens generate microwaves at a frequency of around 2.45 GHz, which is absorbed by water molecules in the food. The absorbed energy causes the water molecules to vibrate and generate heat, effectively cooking the food.
Apart from cooking, microwaves find applications in communication technologies such as satellite communication, radar systems, and wireless networks. They are also used in scientific research, medical imaging, and certain industrial processes.
Infrared Transmission
Infrared waves, also known as IR waves, encompass electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from 300 GHz to 400 THz. These waves find application in short-range communication and rely on line of sight propagation. Unlike some other types of waves, Infrared waves cannot pass through solid objects like walls and can be easily confined within a room. Additionally, they offer a cost-effective and straightforward solution as they do not require any government license for usage. However, it is crucial to consider that IR waves provide a relatively low bandwidth for various purposes.
Laser Transmission
Laser transmission involves the utilization of laser beams to communicate or transfer information. Laser, an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation, emits a concentrated and synchronized beam of light. This characteristic renders lasers well-suited for a wide range of applications in communication and data transmission.
Laser beams are one-way, enabling line of sight propagation in this particular transmission system. Both the sender and receiver sides are equipped with a photo detector and laser. This system provides a high bandwidth at a low cost. However, a disadvantage is that hot turbulent air on sunny days can interfere with the waves and cause the detector to miss them. The main issue with this transmission system is the inability of laser beams to penetrate rain or thick fog.
Employing lasers in communication offers several advantages, including rapid data transfer rates, minimal signal loss, and the ability to transmit over long distances while maintaining signal integrity. Laser communication systems are utilized in various fields, such as telecommunications, space communication (e.g., laser communication between satellites), and optical data links.
Communication Protocol
Communication protocols consist of a series of rules and conventions that dictate the transmission and reception of data between devices within a network. By setting communication standards, these protocols ensure compatibility and facilitate the secure exchange of information. The importance of these protocols cannot be overstated, as they enable seamless communication between devices and systems manufactured by different companies. Here are some communication protocols
Hyper text Transfer Protocol :-
The protocol known as HTTP allows the retrieval of resources, specifically HTML documents. It serves as the underlying framework for all data exchange on the Internet and operates as a client-server protocol, where the recipient (typically the web browser) initiates requests. The complete document is reconstructed by assembling the different sub-documents that are fetched, such as text, layout description, images, videos, scripts, and more. This reconstructed document is then transferred back to the source of the initial request.
 |
| HTTP |
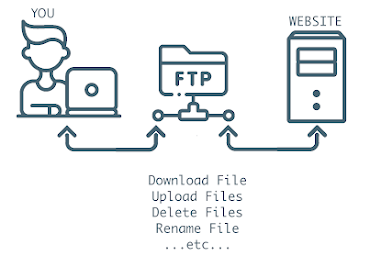
FTP (File Transfer Protocol):-
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is an age-old protocol that remains widely used today. It offers a convenient solution for transferring files. With an FTP server, users gain access to a directory featuring sub-directories. By using an FTP client, individuals can establish connections to these servers, allowing them to download files from the server and upload files to it.
 |
| FTP |
TCP/IP:-
IP:-
 |
| IP |
TCP:-
Serial Line Internet Protocol
Point-to-Point Protocol
PPP, which stands for Point-to-Point Protocol, is a TCP/IP protocol utilized for establishing a connection between two computer systems. This protocol enables computers to communicate over the telephone network or the Internet.
Communication types-Simplex, Half Duplex, Full Duplex
Simplex:
 |
| Simplex |
Half-duplex:
 |
| Half-Duplex-Connection |
Full-duplex:
 |
| Full-duplex |
Modem-Working and characteristics
The term "modem" is derived from the combination of the words modulator and demodulator. Its primary function is to transmit digital data through a telephone line. The transmitting modem converts the data into a signal that can be transmitted over the phone line, while the receiving modem reverses this process by demodulating the signal back into digital data. In the case of wireless modems, they convert digital data into radio signals and vice versa.
 |
| Modulation-Demodulation |
Types of network-client/server and peer-to-peer ,networks,
Client-Server
In this setup, there are multiple clients interacting with a central server. Clients make service requests to the server, which then fulfills these requests. The primary emphasis is on sharing information, with all data being stored on the server side. The client-server architecture is known for its stability and scalability, outperforming peer-to-peer networks due to centralized data management.
P2P
There are no specific server and client roles in this network. Instead, every node functions as both a server and a client. Each node has the capability to request and provide services. The primary objective is to establish connectivity between the nodes. Each node is responsible for storing its own data. However, as the number of nodes increases, the stability of the network may decrease. Furthermore, each user possesses their own data and applications.
 |
| Server-based & Point-to-Point connection |
Types of connections-
Dialup
 |
| Dial-up-Connection |
Leased Lines
What are leased lines?
A leased line is a dedicated data connection with a fixed bandwidth that caters to the needs of data-intensive businesses. This type of connection ensures a reliable and high-quality internet connection, offering guarantees of upload and download speeds, uptime, and resilience. The term "leased" indicates that the connection is rented by the Internet Service Provider (ISP) directly to a business, delivering a level of service that exceeds what standard broadband can offer.
 |
| Leased Line |
Leased lines usually have these distinctive characteristics:
Symmetrical
Leased lines must be symmetrical. This means they have the same upload and download speed.
Uncontended
Leased lines are – by definition – uncontended connections, not shared with other users.
Point to point
They connect two points together, eg the ISP with a business location.
ISDN
What is ISDN?
 |
| ISDN |
DSL(Digital Subscriber Line (DSL))
The telecommunications technology known as Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) provides high-speed transmission to subscribers by utilizing the existing copper wire twisted-pair local loop between the customer premises and the telco's central office (CO).
 |
| DSL |
Types of Network - LAN, WAN, MAN, Internet, VPN
Local Area Network (LAN) –
The purpose of a Local Area Network (LAN) is to establish connectivity among network devices, allowing personal computers and workstations to collaborate by sharing data, tools, and programs. This network is formed by interconnecting a group of computers and devices through a switch or a stack of switches. The LAN employs a private addressing scheme, which adheres to the guidelines set by the TCP/IP protocol.
MAN or Metropolitan area Network --
A MAN, or Metropolitan Area Network, is an intermediate network that has a larger coverage than a LAN but is smaller than a WAN. It enables the connection of multiple computers that are situated in different cities or within the same city. MANs encompass a substantial geographical area and can even serve as an Internet Service Provider (ISP). Nevertheless, the design and upkeep of a MAN network can be a complex task.
 |
| LAN-MAN-WAN |
Wide Area Network (WAN) –
Internet
Conclusion
In conclusion , this blog cover a brief description of following topics
Computer Networks, type of network, Computer Media and different Network Protocols
In summary, I can say that these topics are related to Fundamental of Computer and very helpful for those who pursuing BCA,PGDCA, DCA ,'O' Level Courses from different universities
I hope this blog helps you a lot Happy learning....
Frequently Asked Question(FAQ)
What is Communication ?
The communication process involves a series of steps or actions aimed at achieving successful transmission of information.
What are Component of communication ?
The Component of communication includes contex, sender, message, medium, recipient, feedback .
What are transmission media ?
The transmission medium refers to a conduit through which information can be transmitted from a sender to a receiver.
What is FTP ?
It offers a convenient solution for transferring files.
What is Optical Fiber ?
Optical fiber technology involves the transmission of data through light pulses traveling along a lengthy fiber typically composed of plastic or glass.
What is HTTP ?
It serves as the underlying framework for all data exchange on the Internet and operates as a client-server protocol, where the recipient (typically the web browser) initiates requests.
What is IP ?
The Internet Protocol (IP) acts as the address system for the Internet, playing a crucial role in delivering data packets from a source device to a destination device.
What is TCP ?
The data is transcribed and fragmented into pieces. These pieces are then distributed through separate postal pathways. The TCP protocol serves as an assembler on the receiving end, arranging the pieces in the correct sequence, requesting retransmission of any missing pieces, and informing the sender once the entire message has been received intact.













Post a Comment